Global Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) Tests Market 2015-2030 Featuring Hologic, Roche Diagnostics, Qiagen, Biocare Medical, Abbott Laboratories and Others - ResearchAndMarkets.com - Manchestertimes
Global Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) Tests Market 2015-2030 Featuring Hologic, Roche Diagnostics, Qiagen, Biocare Medical, Abbott Laboratories and Others - ResearchAndMarkets.com - Manchestertimes |
- Global Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) Tests Market 2015-2030 Featuring Hologic, Roche Diagnostics, Qiagen, Biocare Medical, Abbott Laboratories and Others - ResearchAndMarkets.com - Manchestertimes
- Analysis of Ugandan cervical carcinomas, an aid for understudied sub-Saharan women - The Mix
- Cervical Cancer: Symptoms, Treatments, and Outlooks - www.oncnursingnews.com/
- Inovio Pharmaceuticals: A Focus On The HPV Pipeline Candidates - Seeking Alpha
| Posted: 11 Aug 2020 03:19 AM PDT  DUBLIN--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Aug 11, 2020-- This market model is built to visualize quantitative market trends within In Vitro Diagnostics therapeutic area. The model discusses in detail the impact of COVID-19 on Human Papilloma Virus Tests market for the year 2020 and beyond. Factors like favourable government policies, high occurrence rate of HPV infections, and growing cervical cancer screening awareness plans are expected to drive the overall HPV testing market during the forecast period. Genital warts are often caused by non-oncogenic strains of HPV, such as HPV-6 and HPV-11. The HPV tests include NAAT and Other Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) test kits. Each of the covered 39 country's color-coded and fully-sourced market models are equipped with epidemiology based indications with procedure volumes. To increase the data transparency, the interactive excel deliverable covers installed base, new sales volumes, product usage, average selling prices, market size and company share/rank analysis (wherever available). Moreover, analyst comments with qualitative insight offer context for quantitative data. Key Inclusions of the market model are: Currently marketed Human Papilloma Virus Tests and evolving competitive landscape.
Global, Regional and Country level market specific insights.
Drive the understanding of the market by getting the veritable big picture including an overview of the healthcare system. In addition the Market Access segment allows you to delve deeper into market dynamics with information on reimbursement policies and the regulatory landscape.
Robust methodologies and sources enable the model to provide extensive and accurate overview of the market. Demand and supply-side primary sources are integrated within the syndicated models, including Key Opinion Leaders. In addition, real world data sources are leveraged to determine market trends; these include government procedure databases, hospital purchasing databases, and proprietary online databases. Companies covered: Hologic Inc, Roche Diagnostics Corp, Qiagen NV, Biocare Medical LLC, Abbott Laboratories and Others Countries covered: United States, United Kingdom, Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Brazil, China, India, Russia, Japan, Australia, Canada, Mexico, South Korea, Denmark, Ireland, Netherlands, New Zealand, South Africa, Sweden, Switzerland, Austria, Belgium, Finland, Israel, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Taiwan, Czech Republic, Greece, Hungary, Turkey, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Argentina and Chile. Reasons to Buy The model will enable you to:
Laura Wood, Senior Press Manager For E.S.T Office Hours Call 1-917-300-0470 For U.S./CAN Toll Free Call 1-800-526-8630 For GMT Office Hours Call +353-1-416-8900 INDUSTRY KEYWORD: INFECTIOUS DISEASES BIOTECHNOLOGY PHARMACEUTICAL HEALTH SOURCE: Research and Markets Copyright Business Wire 2020. PUB: 08/11/2020 06:19 AM/DISC: 08/11/2020 06:19 AM | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Analysis of Ugandan cervical carcinomas, an aid for understudied sub-Saharan women - The Mix Posted: 10 Aug 2020 12:04 PM PDT This is the first comprehensive genomic study of cervical cancers in sub-Saharan Africa, with a focus on tumors from 212 Ugandan patients. The findings can lead to better treatments.
Now an international team, including Akinyemi I. Ojesina, M.D., Ph.D., University of Alabama at Birmingham, has published the first comprehensive genomic study of cervical cancers in sub-Saharan Africa, with a focus on tumors from 212 Ugandan patients with cervical cancer. Ojesina is one of five researchers who jointly supervised this work, which was published in Nature Genetics. "Large-scale genomics studies like this are important," the co-authors say in the study, "particularly in under-represented ancestry groups, to understand molecular phenotypes of these cancers, which can lead to improved treatment options." "This study is novel as the first cervical cancer study in which the majority of patients were positive for HIV — the virus that causes AIDS," said Ojesina, who is an assistant professor of epidemiology in the UAB School of Public Health, an associate scientist with the O'Neal Comprehensive Cancer Center at UAB and adjunct faculty investigator at the HudsonAlpha Institute for Biotechnology, Huntsville, Alabama. "This allowed identification of genomic features that distinguish HIV-positive and HIV-negative patients." "It is also novel," Ojesina said, "for the identification of unique genomic features associated with the African cohort compared with The Cancer Genome Atlas." The Cancer Genome Atlas includes genomic analysis of many cancers, including 307 cervical cancer tumors from places other than sub-Saharan Africa. Cervical cancer develops in the tissues of the cervix, the narrow lower end of the uterus. Persistent infection by human papilloma virus, or HPV, is necessary, but not sufficient, to cause the cancer. The cancer can be prevented with an HPV vaccine, and it can be detected early by Pap smears. But these resources are scarce in lower- and middle-income areas that have a lot of HIV infections. Genomic analysis of cancers is a complicated business. This study included analyses at many different levels. Researchers started by looking at mutational changes in the DNA of the tumor cells. Restricting that hunt just to locations in the genome that code for expressed portions of genes is a simpler way to search. But the current study, Ojesina said, "is the first cervical cancer study to focus on whole genome sequencing of all samples — as opposed to whole exome — leading to identification of noncoding alterations." Another level of analysis was looking at expression of gene transcripts to see which genes were overexpressed and which were down-regulated. This helps identify pathways used by the tumor to drive cancer growth, and that, in turn, can suggest possible treatments. Part of the expression analysis also involved looking at non-mutational, or epigenetic, changes that can affect gene regulation. These included looking for the addition or removal of methyl groups on DNA bases, or changes in the methylation or acetylation of the histone proteins that help compact the human chromosome. Histone variants that can regulate gene expression were found in various tumors of the Ugandan study.
The current study also found differences among the tumors, depending on whether the HPV was inserted into human chromosomes or not. For HPVs that were inserted into the chromosomes, the locations of the insertions differentially affected gene expression. And finally, the researchers found that certain insertions in the Ugandan tumors led to expression of endogenous retroviral sequences, and upregulation of these sequences was associated with histone modifications. These endogenous retrovirus sequences — found in normal chromosomes — are remnants of ancient retroviral infections that make up about 8 percent of the human genome. Normally they are silenced in human cells, but they can be activated in human disease. Myriad details from all the levels of genomic analysis outlined above are described in the study, "Analysis of Ugandan cervical carcinomas identifies human papillomavirus clade-specific epigenome and transcriptome landscapes." "This international study was funded by the National Cancer Institute Office of Cancer Genomics under the auspices of the HIV+ Tumor Molecular Characterization Project, or HTMCP," Ojesina said. "The bulk of the analysis was done by Marco Marra, Ph.D., and his colleagues at BC Cancer, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. But my team at UAB played a vital role in identifying somatic genomic alterations and unique HPV-associated features. The other UAB personnel involved in the project as members of the HTMCP Cervical Cancer Working group include Vinodh Srinivasasainagendra, Aishwarya Sundaresan and Jianqing Zhang." Besides Marra and Ojesina, joint supervising leaders of the study are Janet S. Rader, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee; Daniela S. Gerhard, National Cancer Institute; and Andrew J. Mungall, BC Cancer. Investigators were drawn from other participating institutions, including the Uganda Cancer Institute, Kampala, Uganda; the National Cancer Institute; Nationwide Children's Hospital, Columbus, Ohio; the University of California at San Francisco; the University of Virginia; Columbia University; the Frederick National Laboratory for Cancer Research, Frederick, Maryland; the Infectious Disease Research Institute, Seattle, Washington; and the Oregon Health and Science University, Portland. Funding for HTMCP came from National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, contracts HHSN261200800001E and HHSN261201500003I. Ojesina was also supported in part by Endlichhofer Trust grant OCCC 3120957 and the V Foundation grant DVP2018-007. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Cervical Cancer: Symptoms, Treatments, and Outlooks - www.oncnursingnews.com/ Posted: 05 Aug 2020 06:37 AM PDT  "The key risk factor for cervical cancer is HPV," Carolyn Grande, CRNP, AOCNP, a medical oncology nurse practitioner at the Abramson Cancer Center Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, said in a presentation at the 4th Annual School of Oncology Nursing virtual meeting. Risk Factors and Symptoms "For most people, the body can clear HPV, but it can be chronic for others – especially those who have higher risk types," Grande explained. She noted that cervical cancer risk factors are similar to the risks of sexually transmitted diseases. This includes:
While most annual cancer screenings start at an older age, the American Cancer Society recommends yearly cervical cancer screenings to start at age 25, with HPV testing every 5 years. And while the disease often starts off as asymptomatic, patients may have symptoms once the cancer grows larger. These can include: bleeding after intercourse, between periods, or after menopause; pelvic pain during intercourse; swelling in the legs; hematuria; problems moving bowels or urinating. Cervical Cancer Treatment Since cervical cancer usually has no early symptoms, it is often diagnosed in later stages, and can be treated with radiation, surgery, and/or chemotherapy. "In terms of cancer treatment in advanced disease, you will have primary chemo radiation. The volume of radiation would be guided by the amount of nodal involvement. In the absence of nodal disease, pelvic radiation, external beam radiation therapy (EBRT) and concurrent platinum-containing systemic therapies and brachytherapy can be options," Grande said. For disease with positive para-aortic and pelvic lymph nodes, cervical cancer is often treated with extended-field EBRT, brachytherapy and concurrent platinum-containing chemotherapy. Metastatic disease, which, unfortunately, is rarely curable, is usually treated with platinum-containing chemotherapy and palliative EBRT. When it comes to drugs commonly used to treat cervical cancer, Grande noted the following:
As treatments evolve and more people take the HPV vaccine, cervical cancer statistics are trending toward the right direction. "Globally, [cervical cancer] is the fourth most common cancer-related death in women. The good news, however, is that the incidence is expected to decline in women who received the HPV vaccine," Grande said. Reference | |||||||||||||||||||||
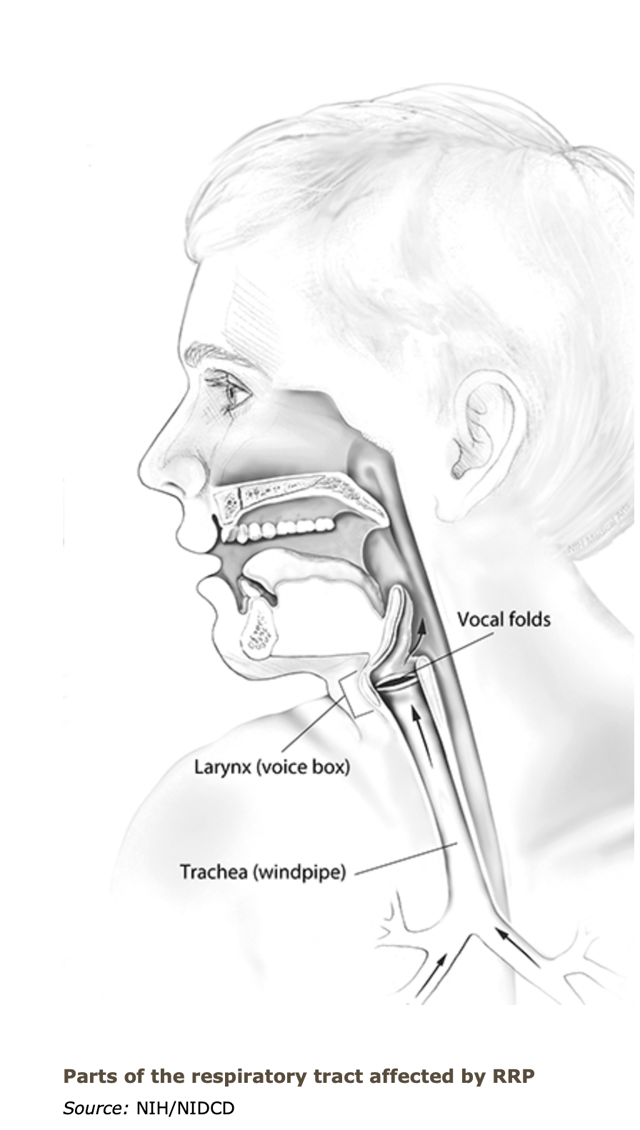
| Inovio Pharmaceuticals: A Focus On The HPV Pipeline Candidates - Seeking Alpha Posted: 02 Aug 2020 12:00 AM PDT Human Papilloma VirusWhile the eyes of the world anxiously await to hear the news of an approved vaccine that is safe, effective and can maintain a durable response for use in the fight against COVID, Inovio continues to plow forward with other indications for urgent health needs in their pipeline such as Anal Dysplasia, Vulvar Dysplasia, Cervical Dysplasia and Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis. Each one of these diseases are a direct result due to exposure and infection to the human pappiloma virus (HPV). The virus is primarily a sexually transmitted disease and all four of the diseases could lead to pre-cancerous lesions which if not treated, can leave a patient with no choice but to undergo various disfiguring surgical procedures. Furthermore, if not treated, these diseases can also lead to cancer and in the most serious cases, death. Inovio's pipeline is addressing the need for a therapeutic vaccine to address these infections caused by (HPV) and investors should be excited about the potential value to Inovio if and when they bring these candidates to market. Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis (RRP) On Wednesday, July 29, 2020, Inovio announced that they had been granted 'Orphan Drug Designation' for INO-3107 to treat a rare disease known as Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis (RRP) caused by the presence of HPV 6 or the HPV 11 virus. Orphan Drug Designation is critical to advancing drug development for rare disease indications, such as RRP.
RRP obstructs patient's airways with primarily benign tumors that can grow in size in the larynx rather quickly requiring invasive surgical procedures and in rare cases, result in cancer. RRP is presently incurable and the courses of treatment include recurrent surgery to remove the tumors as frequently as every few weeks to every few months or the use of antiviral drugs. Regardless of the procedures chosen, living with this incurable disease can result in social isolation as it often comes with a change in voice, hoarseness and difficulty breathing and in the most severe cases, patients opt to insert a permanent tracheotomy.
On February, 11 2020, Dr. Jeffrey Skolnik, Clinical Development Vice President, said this during an interview published in NS Healthcare entitled, "Inovio secures FDA approval for IND clinical trial of INO-3107 to treat RRP",
On February 03, 2020, INO reported results from an investigational pilot clinical study for RRP. INO reported that two out of two (N=2) patients who were teated with INO-3106 were able to successfully delay their semi-annual surgical treatments. One patient's surgical intervention was delayed for over a year and a half (584 days) and the second patient delayed their surgical intervention for over two and a half years (915 days). It should be noted that INO-3107 evolved from INO-3106 in order to treat both, HPV-6 and HPV-11. Anal Dysplasia - Anal Intraepithelial Neoplasia According to the American Cancer Society, anal cancer will claim more than 1,350 deaths in the U.S. and 8,590 news cases (5,900 in women and 2,690 in men) who will be diagnosed in 2020. While the overall risk is approximately 1 in 500, women are more at risk than men. Without treatment, this disease can lead to cancer. Current treatments include surgery, cauterization or laser therapy. Twenty patients enrolled in this study. What is important to note in this study of VGX3100 for the treatment of Anal Dysplasia are the impressive results. Of the twenty patients enrolled in an open label PHII trial, ten of the patients (50%) cleared the pre-cancerous lesions, while fifteen out of twenty (75%) showed a decrease in the number of lesions associated with the disease. Let's repeat that, 50% of the patients "cleared the pre-cancerous lesions". While the population of the study was small, the results once again demonstrates the safety profile of Inovio's DNA SynCon platform.
The PHII clinical trial for Anal dysplasia started in August 2019 and these patients will be followed through week 88 (22 months) or until approximately May 2021. Safety results were consistent with the known safety profile of VGX-3100. There were no drug-related serious adverse events. No cases of carcinoma have been observed. Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia There is much to learn about vulvar neoplasia, but the run down once again shows that there is a connection in women who have HPV. According to the American Cancer Society, these women represent a younger age group while the older age group usually develop a differentiated type VIN, not associated with HPV. Treatment for VIN include the use of topical ointments, such as Imiquimod or topical chemotherapy such as Fluorouracil (5-FU), directly to the skin. Twenty-two (22) subjects enrolled in this study. The primary endpoint of the study is the histologic clearance of high-grade lesions and virologic clearance of the HPV virus in vulvar tissue samples. A look at the interim data on the 10 subjects who completed their primary endpoint evaluation at six months, 80% (8 out of 10 subjects) had a reduction (2 cm2 on average) in qualifying lesion area (average 60% reduction). Two of the ten (20%) completely resolved their VIN with absolutely zero virus detected 6 months following treatment. Worth repeating, as this goes to the bigger picture with the entire VGX3100 platform, 20% cleared the virus altogether with no known HPV infection found. This is terrific considering HPV is the leading cause of Anal, Vulvar, Cervical and RRP diseases. Without HPV, it is unlikely you will develop these diseases and the chances for recurrence are eliminated without HPV. Dr. Robert Edwards, MD, Milton Lawrence McCall Professor and Chair, Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences, University of Pittsburgh and Principal Coordinating Investigator for the trial said this,
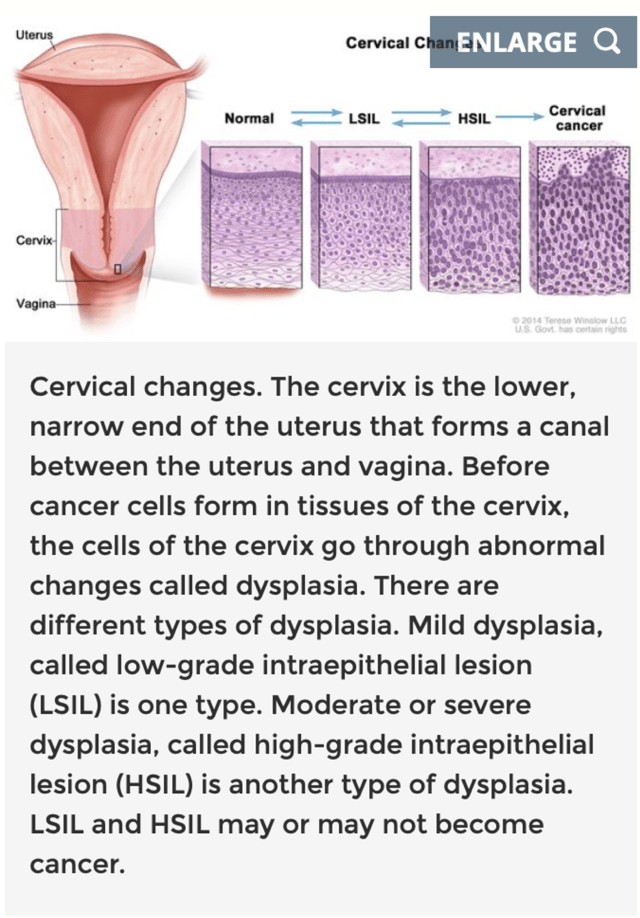
Primary endpoints of this study include the percentage of participants with no histologic evidence of vulvar HSIL and no evidence of HPV-16 and/or HPV-18 in vulvar tissue samples. The expected completion date is Jun 2021. So far, results are consistent with the known safety profile of VGX-3100. There were no drug-related serious adverse events. No cases of carcinoma developing with the patients during this trial have been observed at the time of the report. Readers take note, 'Orphan Drug Designations' are granted in order to treat rare indications, such as RRP, VIN and AIN. The value to Inovio in these designations lies in the incentive for drug development. Tax credits on expenditures incurred in clinical studies, waivers on the New Drug Application (NDA) fee, research grants and awards by the FDA and 7 years of U.S. market exclusivity upon approval for treatments make this designation a valuable designation for any drug maker. Could another application for "Orphan Drug Designation" for AIN and VIN be in the hands of the US Food and Drug Administration? This is something that investors need to carefully monitor as it could provide additional support to the share price. Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia According to the American Cancer Society 13,800 new cases of invasive cervical cancer will be diagnosed in the United States in 2020. Of those, roughly 4,290 women will die from the disease. While regular screening has been beneficial in early detection, it remains a concern. The most frequently diagnosed age group for these women are from the ages of 35-44. Cervical dysplasia is the abnormal growth of pre-cancerous cells on the surface of the cervix. It is usually caused by certain types of HPV. The most common screening process for early detection is through a Pap smear or biopsy. Depending on the duration of the cells infecting the cervix, the symptoms can range from mild, moderate, or severe. Like AIN and VIN, CIN is not cancer in their earliest forms, but may eventually become cancerous and infect other cervical tissue.
Various types of treatments for CIN include permanent and disfiguring surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immuno-therapy. Reproductive health is at risk after many of these procedures and that comes with it's own set of psychological adverse impacts, too. As mentioned, VGX-3100 is a DNA-based immunotherapy under investigation for the treatment of HPV-16 and HPV-18 infection and pre-cancerous lesions of the cervix (phase III) and vulva (phase II) and anal (phase II). Results of the Phase II trials were published in a medical journal The Lancet and the company issued this press release announcing the results. The following was reported,
Worth repeating (immune clearance), VGX3100 was not only found to see a greater statistical decrease in CIN grade 2/3 with women who have been documented with HPV 16 and HPV 18 cervical dysplasia, their treatment decreased lesions AND also cleared the HPV virus infection COMPLETELY vs. the placebo group. The Clinical Trials website indicates that VGX-3100 is currently in PHIII trials and Inovio is running a parallel study. The parallel studies are identified as REVEAL I and REVEAL II. REVEAL I is a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III study delivered intramuscularly followed by (EP) with CELLECTRA™-5PSP for the treatment of HPV-16 and/or HPV-18 related high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) of the cervix with quadruple masking of all trial participants. These include patients (N=200), investigators, care providers and assessors. Primary endpoints include determining the percentage of participants with no evidence of cervical HSIL on histology and no evidence of HPV-16 and/or HPV-18 in cervical samples at Week 36. The expected completion date is April 2021 although the CEO, Dr. Joseph Kim announced that the REVEAL I results will be announced sooner, in late 2020. According to the Clinical Trials website, REVEAL II continues to recruit patients (N=198) however, it can be expected that due to COVID, registering patients has affected registration. REVEAL II is identical in its design as REVEAL I. Investment Risks to ConsiderAs has been discussed, Inovio's CELLECTRA device has not yet been approved by the FDA. The path forward towards approval is based on the FDA's requirements for medical devices. The only question remaining is, can approval be granted after 6,100 uses in over 2,100 patients in controlled clinical settings with no reported serious adverse events? Only the FDA has that answer and so far, approval by the FDA of all Inovio trials, along with the most recent trials for INO-4800 as well as a $71 million dollar award by the Department of Defense in June 2020 to scale up manufacturing of their CELLECTRA EP devices signals the likelihood of approval. Additionally, Inovio remains in ISO compliance and procedures. One piece of good news concerning ISO compliance, as I reported in my last piece was the announcement by the FDA in DEC 2018 that they'll adopt ISO 13485 regulations to replace their own existing medical device quality regulations. This was updated in 2019 and remains pending final adoption. The ISO 13485 certification and the pending adoption by the FDA of ISO 13485 regulations means Inovio's CELLECTRA device is on the path towards likely approval. I'll continue to look for this adoption and report them as they change. The VGXI legal entanglement remains unanswered and as I last reported, is not a gimme, on either side. In fact, it looks as if Inovio intends to continue to pursue all legal remedies available to them. I will not speculate on the outcome, but investors should understand that VGXI, as I said before and from the legal moves made by INO, is a small plasmid manufacturer with a commitment to produce less than 50,000 plasmids for INO-4800. Surely, they can manufacture more but, as of the time of the legal action, only committed to 50,000. On the other hand, Richter-Helms Biologics, Inovio's other contract manufacturer for DNA plasmids, is on track to produce over 500,000 plasmids or 10X VGXI's current contractual contribution and other manufacturers like Ology Biosciences remain in play. Recently, Ology has been labeled as a defendant in the suit by VGXI, based on what evidence VGXI possesses is to be determined. Regardless, Inovio will still be moving forward with their efforts to manufacture 1,000,000 doses of the COVID-19 INO-4800 vaccine before the end of 2020 through manufacturers suited to handle the volume, like Richter-Helm BioLogics. Actionable Conclusions Those who have been watching on the sidelines have seen Inovio consistently demonstrate and deliver, time and time again through their PHI and PHII clinical trials of VGX3100. Not only does VGX3100 treat those with pre-cancerous lesions, but VGX3100 is proving to be an effective therapeutic with a complete clearance of the HPV infection from the patient. No HPV infection after treatment begs the question, "What other HPV illnesses can be targeted bu Inovio and achieve these same results?" While the newest investors entered into the COVID fray by focusing on INO-4800, the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, this article illustrates that there is much more to the Inovio story. The Inovio pipeline is filled with additional candidates for addressing other urgent medical needs including oncology and infectious diseases. These additional candidates will be updated and reported as the details unfold however, that is a statement that is backwards looking. Investors may want to be in the game before the results are reported to capitalize on the potential for capital appreciation, not only for VGX 3100, but other pipeline candidates as well. INO-3107, another VGX3100 HPV product, was granted Orphan Drug Designation. In early pilot trials, patients who received INO-3107 were able to postpone their semi-annual surgical procedures to remove polyps from their voice box (larynx) to periods that exceeded 1.5 - 2.5 years. This treatment and the outcomes are life changing. For more information, readers can visit the RRP Foundation.The announcements of these HPV candidate trials and results continue to excite long time investors. Those who added strictly due to the COVID play may also want to consider adding additional positions in order to discover the potential long term value proposition in Inovio. Upcoming HPV trials results for Cervical Dysplasia, as part of REVEAL I, are due before the EOY, as well as the unblinding for the 18 month overall survival (OS) for Glioblastoma (GBM) using Regeneron's drug, Libtayo combined with INO-5401. Finally, savings lives is in their DNA. One final note: The only favor I ask is that you click the "Follow" button so I can grow my Seeking Alpha readership. This will help me, to help you. Learning and knowledge is a key to investing. It's already difficult for the casual retail investor to find little nuggets of information behind the backdrop of high speed-high frequency investment houses that collate data and trade in milliseconds. My promise is that I will always do my best to provide you with accurate and timely information, when it is submitted to SA."Margin calls provide valuable liquidity to the market." Disclosure: I am/we are long INO. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article. |
| You are subscribed to email updates from "hpv virus" - Google News. To stop receiving these emails, you may unsubscribe now. | Email delivery powered by Google |
| Google, 1600 Amphitheatre Parkway, Mountain View, CA 94043, United States | |
 Cervical cancer kills more than 300,000 middle-aged women a year, and 19 of the 20 nations with the highest death rates are sub-Saharan countries.
Cervical cancer kills more than 300,000 middle-aged women a year, and 19 of the 20 nations with the highest death rates are sub-Saharan countries. 
Comments
Post a Comment